As a result of this configuration the medial pterygoid muscle can exert about 16 times higher force than that produced by the lateral pterygoid muscle. A Novel Treatment for Orofacial Pain Med Ultrason.

Medial And Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Anatomy Download Scientific Diagram
The medial pterygoid is a muscle of your temporomandibular joint and can cause pain in the jaw throat and ear if it is tense or carries trigger points.
. It arises by two heads. The nerve and artery usually pass between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle. The deep part originates on the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate and inserts in the same area of the mandible.
The deep part forms the bulk of the muscle and arises from the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate of. The primary action is to elevate the mandible and laterally deviate it to the opposite side. The medial pterygoid can be very hyperactive in jaw closing dystonia as a result of the so-called whack-a-mole phenomenon after repeated botulinum toxin injections into the masseter and temporalis muscles.
An upper superior and a lower inferior. The medial pterygoid muscle can sometimes be injured during a poor alveolar nerve block due to its being in close proximity to the nerve. Slightly reduced range of opening deviations of mandible with opening altered occlusion my teeth dont fit together right tinnitus are common complaints associated with TrPs in this muscle.
The lateral pterygoid is the big exception in this muscle group in that its fibers run horizontally rather than vertically and one of the two heads of the muscle does not insert into bone but rather inserts into the articular cartilage of the TMJ. These two nerves pass between the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles. The superficial head of the medial pterygoid muscle originates from the maxillary tuberosity of the maxilla and pyramidal process of the palatine bone.
It arises from the pterygoid fossa of the sphenoid bone and the lateral lamina of the pterygoid process and ascends to the inner surface of the mandibular angle and pterygoid tuberosity. However its possible to eliminate these points and tensions with a self-massage. The superior head originates on the sphenoid bone facing the infratemporal fossa.
Authors Yunn Jy Chen 1 Pei-Hsuan Chang 2 Ke-Vin Chang 3 Wei-Ting Wu 4 Levent Özçakar 5 Affiliations 1 Department of Dentistry School of. On this page you will find instructions how to do this. The muscle fibers run posteroinferiorly and laterally surrounding the lower fibers of the lateral pterygoid muscle.
The superficial head is attached to the maxillary tuberosity and the pyramidal process of the palatine bone. The medial pterygoid muscle causes pain in the temporomandibular joint and the ear which increases when you bite down on something. The medial pterygoid nerve is a main trunk from the mandibular nerve before the division of the trigeminal nerve - this is unlike the lateral pterygoid muscle and all other muscles of mastication which are supplied by the anterior division of the mandibular nerve.
This origin is medial to the insertion so can contribute to rotating the mandible causing some side to side movement. Lateral pterygoid medial pterygoid. The pterygoids are often weak and inactive due to the underdevelopment of the maxilla which causes occlusion to establish too posteriorlyThe pterygoids pro.
Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need. On the lateral side superficial surface the lateral pterygoid muscle relates to the mandibular ramus maxillary artery temporalis tendon and the masseter muscle. The deep head is the major component and is attached to the medial aspect of the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
Protrusion depression medial movement of mandible. Pterygoid branches of the maxillary artery. The medial and lateral pterygoids move the mandible from side to side and also protrude the mandible.
The deep head of the muscle originates from the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone. Ultrasound Guided Injection for Medial and Lateral Pterygoid Muscles. Medial and Lateral Pterygoids are both well hidden by the lower jaw bone.
On the medial side deep surface the muscle is related to the mandibular nerve the middle meningeal artery the sphenomandibular ligament and the upper part of the medial pterygoid muscle. The lateral pterygoid is a short thick muscle somewhat conical in form which extends almost horizontally posteriorly and laterally between the infratemporal fossa and the condyle of the mandible. Where is the jaw muscle.
Both heads originate anterior to the insertions so like the superficial head of the masseter it is. Protrusion elevation medial movement of mandible. Jaw opening jaw deviation and jaw protrusion types of oromamdibular dystonia are caused by involuntary contraction of the lateral pterygoid muscles.
The medial pterygoid muscle is separated from the superior pharyngeal constrictor by two muscles. Using the medial and lateral pterygoid muscles as references identify the buccal branch of the mandibular nerve CN V3 and accompanying buccal artery. You will also learn.
Like the medial pterygoid and the masseter it has two heads. It has two heads of origin. Superficial and deep that are separated by the inferior head of lateral pterygoid muscle at their origin.
The medial pterygoid muscle is characterized by short muscle fibers and large physiological cross-sectional area in comparison to other pterygoid muscle lateral pterygoid. Lateral pterygoid TrPs Refer often severe pain into the maxillary sinus deeply into the TM joint produce dysfunctions of the joint. The primary action is to elevate the mandible and laterally deviate it to the opposite side.
The medial pterygoid lies on the medial side of the mandible as a mirror image of the masseter. Your masseter muscle is your primary chewing muscle not the only one1 but the main one and it covers the sides of the jaw just behind the cheeks. The medial pterygoid muscle attaches to the angle of the mandible and to the lateral pterygoid plate to form a sling with the masseter muscle that suspends the mandible Figure 6-19.
The medial pterygoid muscle is a thick and square shaped muscle. It can assist in protrusion of the mandible. The medial pterygoid muscle attaches to the angle of the mandible and to the lateral pterygoid plate to form a sling with the masseter muscle that suspends the mandible Figure 6-19.
Branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve CN V3 Blood supply. Medial pterygoid muscle consists of two heads. It can assist in protrusion of the mandible.

Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Medial Pterygoid Muscle Temporal Muscle Masseter Muscle Pterygoid Processes Of The Sphenoid Others Angle Head Anatomy Png Pngwing

Medial Pterygoid Learn Muscles

Musclemonday Pterygoid Muscles Today We Are Going To Discuss Our Last Muscle Of The Week The Medial And Lateral Muscle Health And Wellness Physical Therapy

Pterygoid Muscles Illustration Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Mnemonic Lateral Pterygoid Vs Medial Pterygoid Function Urdu Hindi Youtube
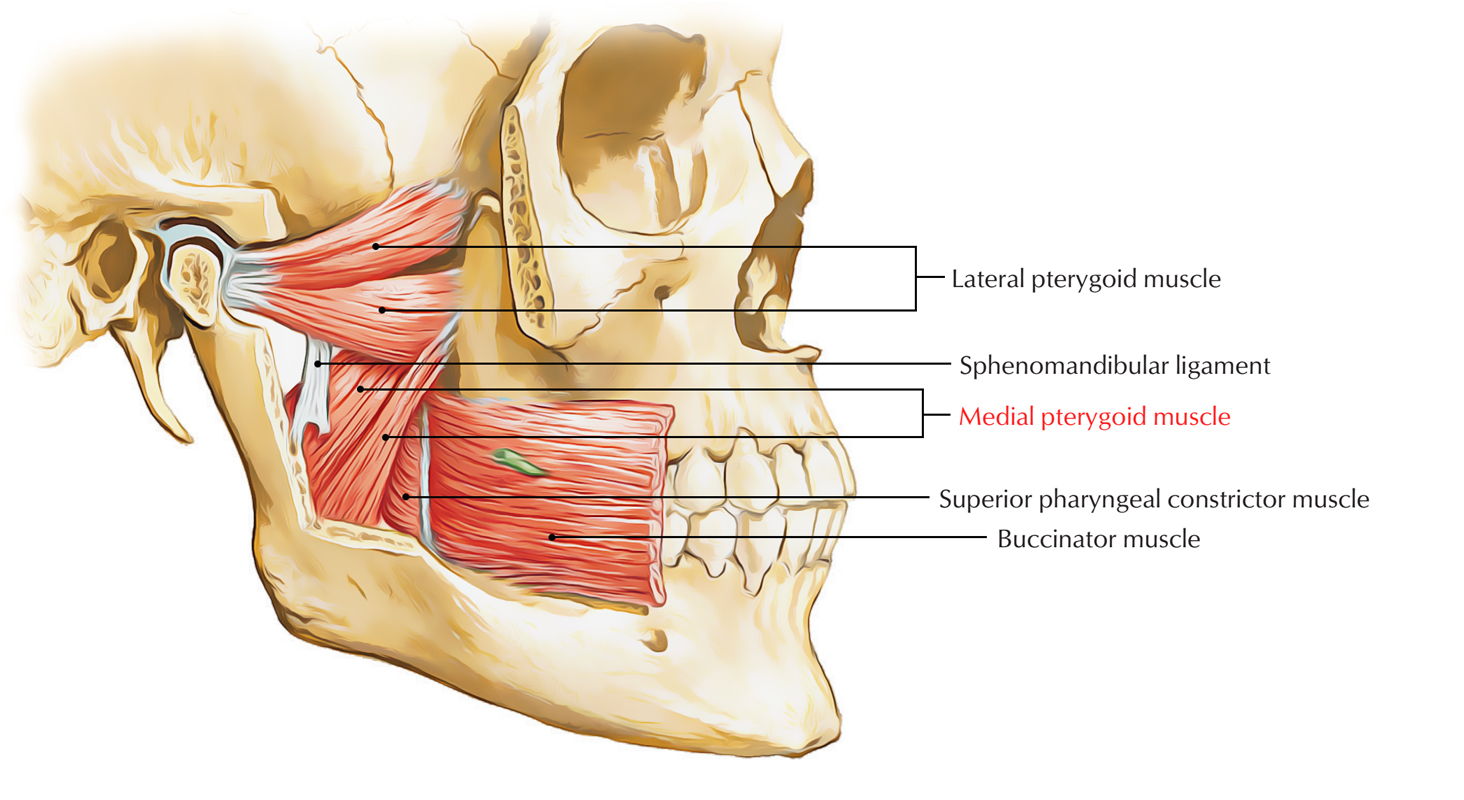
Medial Pterygoid Muscle Earth S Lab

Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Wikipedia
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14110/Pterygoid_muscles.png)
Medial And Lateral Pterygoid Muscle Anatomy And Function Kenhub
0 comments
Post a Comment